>Corresponding Author : Benhaddouga Khadija
>Article Type : Case Report
>Volume : 5 | Issue : 7
>Received Date : 04 July, 2025
>Accepted Date : 14 July, 2025
>Published Date : 18 July, 2025
>DOI : https://doi.org/10.54289/JCRMH2500131
>Citation : Benhaddouga K, Daoudi S, Hind M, Chyate FZ, Mediani H, et al. (2025) Pregnancy on Uterine Scar: 1 Case Report and Review of the Literature. J Case Rep Med Hist 5(6): doi https://doi.org/10.54289/JCRMH2500131
>Copyright : © 2025 Benhadouga K, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Case Report | Open Access | Full Text
1Resident Physician, Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, at Ibn Rochd University Hospital, Casablanca, Morocco
2Professor in the Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics at the Ibno Rochd University Hospital in Casablanca, Morocco
*Corresponding author: Benhadouga Khadija, Resident Physician, Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, at Ibno Rochd University Hospital, Casablanca, Morocco
Abstract
Uterine scar pregnancy is a rare form of ectopic pregnancy that occurs at the site of a previous caesarean section scar. With the global increase in caesarean section rates, this pathology is tending to become more frequent. It constitutes a diagnostic and therapeutic emergency, due to the high risk of serious complications such as uterine rupture, massive hemorrhage and loss of fertility. Diagnosis relies mainly on transvaginal ultrasound, and treatment varies according to the patient's clinical condition and desire for future fertility. Prevention involves carefully limiting the indications for Caesarean sections and rigorously monitoring patients at risk. Early and appropriate management can significantly improve prognosis.
Keywords: Scar Pregnancy, Ectopic Pregnancy, Cesarean Section, Uterine Niche, Transvaginal Ultrasound, Uterine Rupture, Fertility, Methotrexate, Management, Prevention
Introduction
Caesarean section is the most common obstetric procedure in the world, with a steadily rising rate, averaging 21% of births worldwide, and sometimes exceeding 30% in some middle- and high-income countries [1]. This rise can be explained by a variety of factors, including increased medicalization of childbirth, maternal preferences and local clinical practices. However, this trend is accompanied by an increase in uterine scar-related complications, notably scar pregnancy, a rare form of ectopic pregnancy implanted at an old uterine incision [2]. Although uncommon, this condition represents a major risk of uterine rupture, severe haemorrhage or even hysterectomy, and seriously compromises subsequent fertility [3]. In this context, it is essential to understand the mechanisms, diagnosis and management of this condition.
Case Report
The patient was a 33-year-old mother of 2 live children by Caesarean section, presenting with pelvic pain.
Her history of the disease dates back 2 months to moderate metrorrhagia with delayed menses.
- BHCG (05/09/2024): 37 184 mUI/mL
- Pelvic ultrasound (09/09/2024): (figure 1)
- The uterus is enlarged, measuring 11.5x53x72 mm
- Seat of a 33 mm supra-isthmic ovarian sac, hypotonic, containing an embryo with no active movement or cardiac activity.
- Monoembryonic intrauterine pregnancy arrested at 07 weeks amenorrhea and 03 days
- Associated moderate corporal intracavitary hematometry measuring 43x14mm
- Pelvic ultrasound (09/25/2024) (figure 2): globular uterus with hypotonic intra cavitary gestational sac with isthmic projection and embryo without AC, LCC of 11mm corresponding to 7SA.
- 09/09/2024 > GA 8SA+4J [DDR corrected 11/07/2024]
- Patient expelled in late September 2024
- Presented with pelvic pain isolated for 3 days with no associated metrorrhagia.
Clinical examination: unremarkable
Pelvic ultrasound (figure 3): isthmic pregnancy on uterine scar
Biological workup: BHCG: 15mUI/mL vs 37,184 mUI/mL on 05/09/2024
HB: 11.4 g/dL WBC: 5,630/mm Plq: 16,9000/mm CRP: 6.1
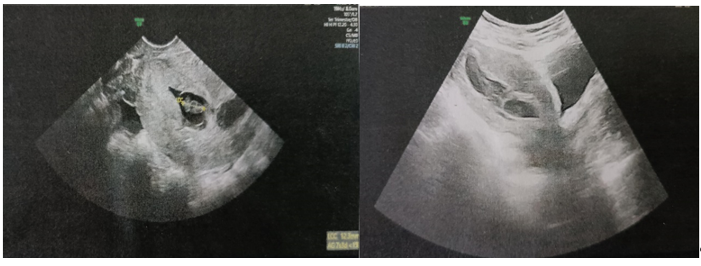
Figure 1: Isthmic Gestational Sac Containing an Embryo with no Cardiac Activity
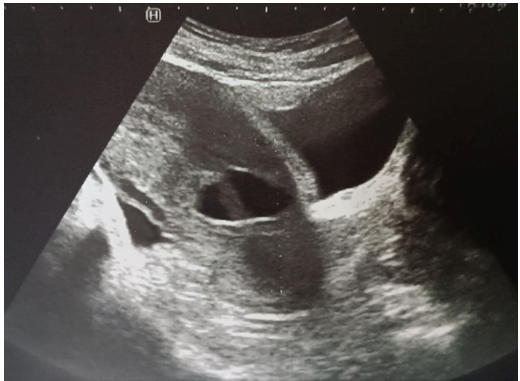
Figure 2: Gestational Sac with Isthmic Projection Containing an Embryo with no Cardiac Activity
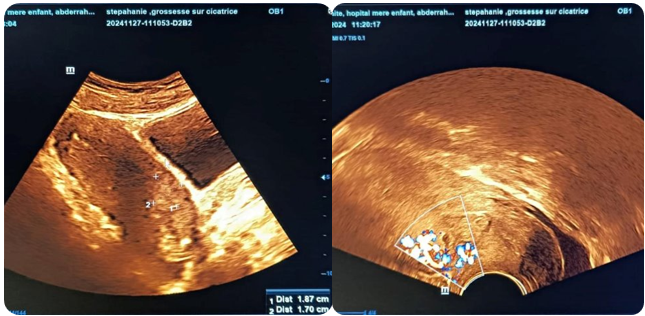
Figure 3: Isthmic Pregnancy on Uterine Scarring
Discussion
Scar pregnancy is a rare complication, with an estimated incidence of between 1/1800 and 1/2216 pregnancies [4]. It is defined by the implantation of the gestational sac in the thickness of the myometrium, at the level of a previous caesarean section scar. This abnormal location is often favoured by poor uterine healing, forming a dehiscence or “niche” which allows the blastocyst to implant in poorly vascularized fibrous tissue [5].
Diagnosis relies mainly on endovaginal ultrasound. This shows a gestational sac in the anterior part of the uterine isthmus, separated from the endometrial cavity, with a thinned myometrium between the sac and the bladder [6]. Color Doppler may show peri-gestational hypervascularization. MRI can also be used to determine the extent of myometrial invasion, particularly if surgery is envisaged.
The clinical consequences are potentially severe: early uterine rupture, massive hemorrhage, arterial embolization or even hemostatic hysterectomy [7]. At a more advanced stage, some pregnancies may progress to placenta accreta, increta or percreta, particularly if not terminated early [8].
Management depends on several factors: gestational age, hemodynamic status, desire for future pregnancy and available resources. There are several options: medical treatment (with systemic or local methotrexate), ultrasound-guided surgical aspiration, hysteroscopic or laparoscopic resection, or even uterine artery embolization [9]. A conservative approach may be proposed in the case of very early diagnosis, but close monitoring is essential due to the high risk of complications. In the case of late-diagnosed progressive scar pregnancy, some teams have proposed an expectant approach until viability, with planned caesarean section, but the risk of maternal morbidity remains high [10].
Prevention relies primarily on limiting non-medically justified caesarean sections [1], as well as ultrasound evaluation of uterine scars postpartum and at the start of subsequent pregnancies. Some studies suggest that surgical repair of scar niches may reduce the risk of scar pregnancy, although evidence remains limited [11].
Conclusion
Uterine scar pregnancy is a rare but serious complication of previous caesarean sections. Diagnosis relies on early transvaginal ultrasound, and management requires a multidisciplinary approach, tailored to the clinical context. Prognosis is highly dependent on early diagnosis and rapid management. It is imperative to promote sensible obstetric practices to limit the overuse of caesarean sections [1], and to ensure careful follow-up of patients at risk. Finally, further research is needed to assess the efficacy of conservative treatments, niche repair techniques and implications for future fertility [11].
Reference
- Betrán AP., Ye J., Moller AB., Zhang J., Gülmezoglu AM., Torloni MR. The Increasing Trend in Caesarean Section Rates: Global., Regional and National Estimates. PLoS ONE. 2016;11(2):e0148343. [PubMed.]
- Timor–Tritsch IE., Monteagudo A., Cali G., D’Antonio F. Cesarean scar pregnancy: diagnosis and pathogenesis. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2019;46(4):797–811. [PubMed.]
- Vial Y., Petignat P., Hohlfeld P. Pregnancy in a cesarean scar. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2000;16(6):592–3. [PubMed.]
- Rotas MA., Haberman S., Levgur M. Cesarean scar ectopic pregnancies: etiology., diagnosis., and management. Obstet Gynecol. 2006;107(6):1373–81. [PubMed.]
- Seow KM., Huang LW., Lin YH., Lin MY., Tsai YL., Hwang JL. Cesarean scar pregnancy: issues in management. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2004;23(3):247–53. [PubMed.]
- Jurkovic D., Hillaby K., Woelfer B., Lawrence A., Salim R., Elson CJ. First–trimester diagnosis and management of pregnancies implanted into the lower uterine segment cesarean section scar. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2003;21(3):220–7. [PubMed.]
- Maymon R., Halperin R., Mendlovic S., Schneider D., Herman A. Ectopic pregnancies in cesarean section scars: the 8 year experience of one medical center. Hum Reprod. 2004;19(2):278–84. [PubMed.]
- Timor–Tritsch IE., Monteagudo A. Unforeseen consequences of the increasing rate of cesarean deliveries: early placenta accreta and cesarean scar pregnancy. AJP Rep. 2012;2(1):35–41. [PubMed.]
- Birch Petersen K., Hoffmann E., Rifbjerg Larsen C., Svarre NH. Cesarean scar pregnancy: a systematic review of treatment studies. Fertil Steril. 2016;105(4):958–67. [PubMed.]
- Osser OV., Jokubkiene L., Valentin L. High prevalence of defects in cesarean section scars at transvaginal ultrasound examination. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2009;34(1):90–7. [PubMed.]
- Wang CJ., Huang HJ., Chao AS., Chao A., Wang CW., Soong YK. Efficacy of hysteroscopic repair of cesarean scar defects in women with abnormal uterine bleeding. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2009;16(3):363–6. [Ref.]